--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: Introduction to the Universal GL.
• Replaces multiple tables: The Universal Journal consolidates data from various financial and controlling components (like FI, CO, Asset Accounting, and Material Ledger) into a single table called ACDOCA.• Single source of truth: By storing all relevant data in one place, it eliminates reconciliation efforts between different modules and ensures data consistency. The SAP Universal Journal, a core component of SAP S/4HANA, streamlines financial and management accounting by consolidating data from previously separate modules into a single source. This leads to improved efficiency, faster reporting, and enhanced insights into financial performance.• Real-time analytics: The Universal Journal enables real-time financial analysis and reporting, as all data is readily available in a single source.• Improved efficiency: It simplifies financial processes, reduces data redundancy, and optimizes system performance. By eliminating data redundancy, the Universal Journal helps reduce the overall memory footprint of the SAP system. The unified data structure also allows for more efficient storage of financial data, optimizing system performance.
Case Example: Imagine a sales transaction. In traditional SAP, you might have entries in FI (for the revenue) and CO (for the cost of goods sold). With the Universal Journal, these entries are recorded once in ACDOCA, eliminating the need for reconciliation and providing a unified view of the transaction.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
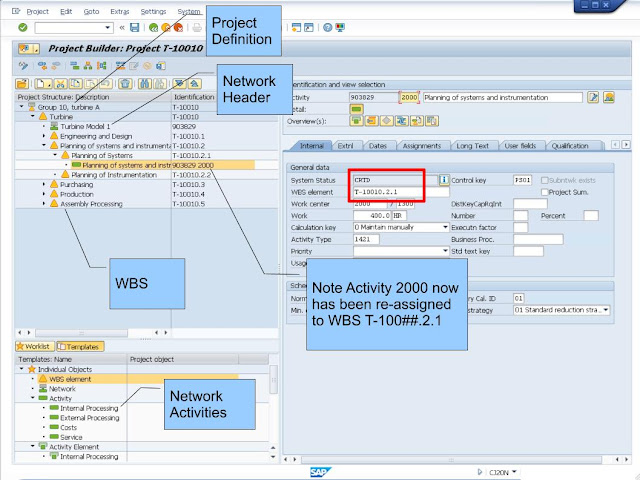
Question: Project Structure introduction, create Project using Copy from Function in CJ20N.
Answer: SAP transaction code CJ20N, known as the Project Builder, is a central transaction within the SAP Project System (PS) module. It is used for creating, changing, and displaying project structures, including work breakdown structures (WBS elements) and networks. CJ20N provides a comprehensive interface for managing all aspects of a project within SAP.
• Project Definition: CJ20N allows users to create and manage project definitions, which serve as the overarching framework for the project.• Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Users can create and maintain WBS elements, which break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks or deliverables.• Networks: CJ20N facilitates the creation and management of networks, which define the relationships and dependencies between activities within the project.• Assignments: It allows for the assignment of various elements within the project, such as materials, costs, and resources, to specific WBS elements or activities.• Planning: CJ20N supports planning activities, including scheduling, cost planning, and material planning.• Release: Users can release the project or specific parts of it, signaling that they are ready for further processing or execution.• Display: CJ20N provides a display function for reviewing project structures, activities, and assignments.
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2014/06/create-project-copy-from-standard.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: What are the Main "Elements" in an SAP PS Project Structure:
Answer: Here are some details of the Main "Elements" of SAP PS Structure explained in class:
• Project Definition:
• In SAP, the highest level WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) element is the Project Definition. It represents the overall project and serves as the top-level container for all other WBS elements within that project.
• The Project Definition includes data that is binding for the entire project, ensuring consistency and control across all project activities. And that is why it is assigned with the Project Profile which contains the Overall Profile (Mother Profile) of all other Profles for Project Logistics and Project Accounting in the WBS and Network Structuring.
• WBS (Work Breakdown Structure):
• A hierarchical representation of the project, breaking it down into smaller, manageable tasks or work packages.• Each level in the hierarchy represents a more detailed level of the project.• Individual elements within the WBS are called WBS elements.• WBS elements can be assigned to network activities to link them to the overall project structure.
• Highest Level WBS:
• Just "below" the Project Definition, it is highly recommended to have only ONE WBS to represent the WBS "Header" for the rest of the WBS structuring below it.
• One of th advantage of the TOP WBS is also to be able to final all lower level WBS costs to the Highest level WBS to present the total Project Costs before the final settlement.
• Network:
• Represent the flow and dependencies between project activities.• Consist of activities (individual tasks) and relationships (dependencies between activities).• Facilitate planning, scheduling, and monitoring of project timelines and resource allocation.• Can be linked to WBS elements to integrate the network activities with the overall project structure.
• Network Header:
• The Network Header acts as a central control point for a network, which is a specific type of work order. It contains default organizational assignment data and control information that applies to the entire network, similar to how a project definition applies to a work breakdown structure (WBS). Think of it as the "header" for all activities within a network.
• Network Activities:
• a Network activity represents a specific task or piece of work within a project network. It's a fundamental building block used for planning, executing, and monitoring project progress, resources, and costs. These activities are linked together to form the network, which outlines the sequence and dependencies of project tasks.
• Network activities can represent various types of work using the "Control Key", including:
• Internal Processing: Tasks performed by internal resources within the company. (via Confirmations)• External Processing: Tasks outsourced to external vendors. (via PR-PO-GR)• Service Activities: Procurement of external services. (via PR-PO-Service Entry)• Cost Activities: Activities that primarily involve costs, such as travel expenses. (via Cost Allocation)
SAP Official References:
https://www.sap.com/assetdetail/2023/04/SAP Project System Overview/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: Review on PS Network Relationships.
Answer: In SAP Project System (PS), a network relationship defines the logical sequence and time-based dependencies between activities within a project. It essentially establishes how activities relate to each other, indicating which activities must precede or follow others. These relationships are crucial for planning, scheduling, and controlling project timelines and resource allocation.• Purpose: Network relationships in SAP PS are used to model the workflow of a project, showing the chronological order in which activities must be performed.• Types: Common relationship types include:
• Start-to-Start (SS): One activity's start triggers the start of another.• Start-to-Finish (SF): One activity's start triggers the finish of another.• Finish-to-Start (FS): One activity's finish triggers the start of another (most common).• Finish-to-Finish (FF): One activity's finish triggers the finish of another.
• Graphical Representation: Relationships can be visualized in a network diagram, allowing project managers to see the overall flow and dependencies.• Importance: By defining relationships, SAP PS can automate scheduling, resource allocation, and cost tracking, ensuring that project activities are executed in the correct order and within the specified timelines.
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2014/06/sap-project-system-create-activity.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: Review PS Text, DMS Document assignment, and Milestone assignment to SAP Project System Structure.
Answer: Additional assignments possible to WBS and Network Activities are Milestones, PS Text, and DMS Documents:
• Milestones: In SAP Project System (PS), milestones represent key points in a project's lifecycle, signifying the completion of specific tasks or phases. They are crucial for tracking progress, managing resources, and triggering events like billing or workflow actions.
• PS Text: In SAP Project System (PS), PS texts are user-definable texts that provide additional information about project elements like WBS elements or activities. These texts can be used to store details like requirements definitions, work package descriptions, or logs. They are managed in a PS text catalog and can be created in various formats, including SAPscript and external documents like Word, Excel, or PowerPoint files.• DMS Documents: SAP DMS documents refer to electronic documents and digital assets managed within the SAP Document Management System (DMS). SAP DMS is a comprehensive system for storing, managing, and tracking documents throughout their lifecycle, supporting various file types and integrating with other SAP modules, and in this case to the PS WBS and Network Activities.
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2014/06/sap-project-system-create-ps-text.html
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2014/06/sap-project-system-create-milestones.html
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2014/06/sap-project-system-perform-mass-change.html


.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.