This Blog is mainly on SAP Exam Questions and Selected "How-to" SAP processes
Sunday, July 28, 2024
Thursday, July 25, 2024
Sunday, July 21, 2024
Question no 4009 : Splitting requirement quantity to Supplier or Production Version based on the Quota
(only one answer)
A. EX
B. ES
C. FX
D. FS
E. SP
.
Answer: B
"ES" Lot for Lot with Split
Saturday, July 20, 2024
Q&A in Class (2024-07-17) S4220
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: For participants who are new to the MRP techniques!
Answer: Material requirements planning (MRP) is a system for calculating the materials and components needed to manufacture a product, and it all started in the 1960s. Many software started with the MRP system with integrations of Logistics and Finance for an End-to-End process, AND it is later in the 1980s-1990s that MRPII and later ERP with infusion of Capacity and other business components into an Enterprise Solution.
As in the past, MRP software vendors today are taking advantage of new technologies to improve their products and offer more capabilities to users. Foremost on the list is the application of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) in advanced planning processes to allow the systems to develop even better plans and schedules. Machine learning-enabled planning systems continually monitor conditions and activities to develop more precise models on cause and effect – so that its future recommendations are more comprehensive, more precise, and more effective.
https://froggysap/SAP_MRP_Mechanics(1)
https://froggysap/SAP_MRP_Mechanics(2)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: in MRP 1 view's Assembly Scrap Factor, what is the purpose?
Answer: Scrap Factors are used to represent "wastage" or "handling errors" or "production problems" resulting in component or assembly wastage. The various Scrap Factors can be setup in MRP1, MRP4, BOM Component Detail or Operation Detail; all uses to increase the Quantity of Procurement (internal or external) for Assembly or Components to cater for possible wastages. The settings are also used for Cost Estimates for the Assembly and Component.
There are 4 scrap factors:
- Assembly Scrap Factor in Material Master MRP 1 view
- Component Scrap Factor in Material Master MRP4 view
- Operation Scrap Factor in Routing Operation
- Net ID for Operation/Component Scrap Factor in BOM Component Detail
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2019/10/set-scrap-factors-in-production.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: What is the use of the Backflushing indicator in the Material Master MRP2 view?
Answer: Backflushing means at the point of Goods Receipt of Production Order, the system will also perform Goods Issues at the same time; this simultaneous GR and GI is called Backflushing.
click link to check a demo of Staging and Backflush with PP-EWM integration:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: Explain the use of Co-Products in the MRP2 view?https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2019/08/co-products-for-production-orders.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: Explain the formula in SAP on the calculations of ROP and Safety Stocks.--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: What is the purpose of the Takt Time indicator in the MRP 1 view of the Material Master ?
Answer: The Takt time is used in conjunction of the Lot Size Key with either Forward (+) or Backward (-) Overlapping, to allow MRP run to create a "staggered" Qty of delivery from the Supplier instead of a Single Qty delivery. Some of the reason for this is Warehouse capacity or Production do not required ALL the Materials to be delivered on ONE Day as the Production is also spread to multiple days.
Notice in the above, the Takt time is 1 day with Lot Size key "ZF" ("-" indicating Backward Overlap) plus a Fixed Lot Size of 50. Note in the 2nd slide that the Requirement 100 is split into 2 Planned Orders each of 50 due to the Fixed Lot Size but one of the Planned Order's expected delivery is backward 1 day earlier DUE to the Takt Time of 1 day plus the Backward Overlapping setting.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: To show the setup of processing steps for Planning at Sub-Assembly level Strategy "70".
Answer: This SAP Planning Strategy "70" is particularly useful when there are multiple (many) variants of Finished Goods that are produced using Common Sub-Assemblies. Due to too many variants, the Forecast (PIR) may not be possible at the Finished Goods level and the Strategy "70" to be assigned to the Sub-Assembly level will allow the PIR to be created for the Common Sub-Assembly level.In SAP, there are 2 Planning Strategies for the Su-Assembly level ("70" for MTS and "74" for MTO). BUT, for Strategy "70", it will support Finished Goods with Strategy MTO or MTS. You can see how this works in the Blog Posts below.
click to google drive for the calculation step for ROP and SS in SAP:
https://docs.google.com/presentation/strategy70/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: PIR's "Regular Supplier", Source List in S/4HANA with the new in S/4's PIR's "Auto Sourcing".
Answer: The "Regular Vendor/Supplier" indicator was introduced to the Info Record in SAP R/4 version 4.0 to be used without a Source List so that Source Determination at Purchase Requisition can be done without a Source List. In this case, as long as only one of the PIR (Info Record) same Material but different Vendor AND only ONE PIR has the "Regular Vendor", this PIR will be selected at Source Determination for PR creation at ME51N. (this is done without a Source List".
In S/4HANA, due to Simplification project, SAP introduce the "Auto Sourcing" indicator in the Info Record allowing Automatic Source Determination at MRP run AND again negating the need for a Source List. This is possible as long as only ONE Info Record for SAME Material Different Vendor has the "Auto Sourcing" indicator.
HOWEVER, it is important to note that the SOURCE LIST is NOT no longer useful. FOR, if the USER creates a SOURCE LIST, then it will still be RESPECTED for Source Determination at all situations like Source Determination for PR creation as well Source Determination at MRP run. For example, if the "Auto Sourcing" or "Regular Vendor" is set at the Info Record BUT the Source List was SET to "BLOCK" the Vendor; the associated Vendor is NOT selected at Source Determination.
https://docs.google.com/presentation/regular_vendor/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: Predictive MRP explain again.
Answer: in ECC, simulation can be done only via LTP (Long Term Planning) which can ready PIR of either Active or non-Active Version in an LTP scenario. The classic LTP allows the Planner to simulated the PIR's capacity situation for Finished Products and Sub-Assemblies. Mid or Longer Term Purchasing Plan can be written into Purchasing Info System for Procurement Negotiations. When the non-Active PIR in simulation in LTP is found to be accepted, then it can be activated.
pMRP is a new functionality available only via FIORI App by SAP in S/4HANA to help the user to identify potential capacity issues and to evaluate possible solutions as early as possible based on a simplified requirements plan using a simplified material requirements algorithm.Question: to explain DDMRP concept again.
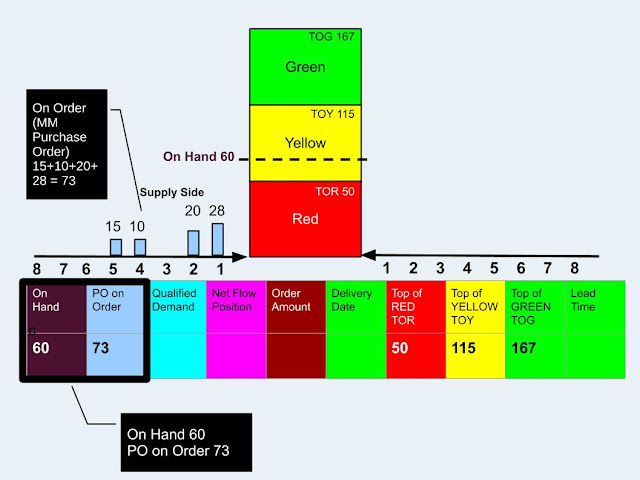_Blogged.jpg)
click here to view the basic logic of DDMRP:
https://docs.google.com/presentation/DDMRP_Mechanics/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question: Show demo examples of SAP Quota Arrangement applications in SAP.click below to see examples of applications of SAP Quota Arrangement:
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2014/07/mrp-quota-arrangement-max-lotsize-1x.html
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2014/01/mrp-quota-arrangement-min-lot-size.html
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2016/07/material-management-supplier-capacity.html
https://froggysap.blogspot.com/2016/04/pp-rem-quota-arrangement-line-load-via.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Friday, July 19, 2024
Monday, July 15, 2024
Sunday, July 14, 2024
Saturday, July 13, 2024
Friday, July 12, 2024
Question no 4008 : Schedule Line Category determination
(only one answer)
A. Item Category and MRP Group.
B. Material Type and MRP Type.
C. Item Category and MRP Type.
D. Order Type, Item Category and MRP Type.
E. Order Type, Item Category, and MRP Group.
Answer: C
SPRO > Sales & Distribution > Sales Documents > Schedule Lines
Thursday, July 11, 2024
Wednesday, July 10, 2024
Tuesday, July 9, 2024
Monday, July 8, 2024
Sunday, July 7, 2024
Saturday, July 6, 2024
Question no 4007 : Info Record Characteristics
(more than one answers)
A. Vendor
B. Plant
C. Purchasing Organization
D. Material Master
E. Material Type
.
Answer: A, C
A, C) An Info Record with only Vendor and Purchasing Organization is a Material Group info Record without Plant.
B) A Plant is not necessary for an Info Record as when the Company is able to negotiate prices from the Supplier regardless of the Plant.
D) When a Material Master is not entered for an Info Record, it can be a Material Group Info Record.
Friday, July 5, 2024
Wednesday, July 3, 2024
Tuesday, July 2, 2024
Monday, July 1, 2024
Question no 4006 : Purchasing Central Contract
(more than one answers)
A. The Central Contract is created without a Plant.
B. Plant specific Conditions are possible.
C. The Purchasing Organization for the Central Contract can be different from the Purchasing Organization that issue the Purchase Order Release against the Contract.
D. Same or different Contact Validity Periods are required to be entered for each Contract items.
E. Both Quantity Contract and Value-based Contract can be created for a Central Contract.
Answer: A, B, C, E
A) TRUE.


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
_Blogged.jpg)

.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

_Blogged.jpg)
_Blogged.jpg)






.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)